April is National Donate Life Month. April 16 is National Healthcare Decisions Day.
Emergencies, including personal injury and illness, are often unpredictable. That unpredictability is both a reason to prepare and something to prepare for.
Plan Ahead for Personal Health Emergencies
Many people face decisions about treatments that a medical emergency might leave them incapable of making.(1)
Advance care planning is an important preparedness step toward making sure you get the medical care you would want if you cannot speak for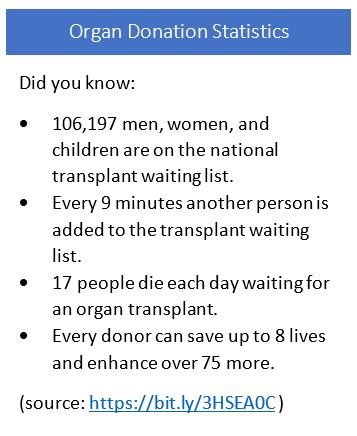 yourself.(2)
yourself.(2)
While you might prefer to think that you will never need such a plan, advance care planning is a way to care for others if you get ill or are injured.
Advance care planning is not just for older adults. At any age, a medical emergency could leave you too ill or injured to make your own health care decisions.
Advance care planning can save loved ones from confusion, family infighting, and second-guessing if they made the right decisions on your behalf.(3)
Advance care planning involves several steps:
- Learn about the types of healthcare decisions that you might need to make.
- Consider those decisions ahead of time.
- Make your decisions known to others.
Talk to family and a doctor as part of your advance care planning. They can help you understand the choices you may need to make and think through your decisions before you put them in writing.(4)
Organ Donation
Organ donation is one of many important decisions you can make as part of your advance care planning for medical emergencies. Others include deciding when you want emergency medical professionals to use cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) or an automated external defibrillator (AED) to restart your heart.
Organ donation is the process of taking healthy organs and tissues from one person for transplantation into another. Organs you can donate include:
- Internal organs: Kidneys, heart, liver, pancreas, intestines, lungs
- Skin
- Bone and bone marrow
- Cornea(5)
Learn more about how donation works and the difference you can make when you become an organ donor.
Become a Donor
Anyone can sign up to be an organ donor regardless of age, race, ethnicity, religion, or health status. It only takes a few minutes. Sign up online through your state registry or in person at your local department of motor vehicles. Your donation can save or improve more than 80 lives.(6)
You can update your information on your state’s online donor registry at any time. Most states let you choose which organs and tissues you want to donate.(7)
Make Your Decisions Known
Preparedness isn’t a prediction of the future. There’s no guarantee that you’ll need advance care planning. You may never need others to make healthcare decisions on your behalf.
Once you’ve come to decisions on things like organ donation, you should talk to your family about your decisions and write them down. There are several ways to do that.
Advanced directives, including living wills, are legal documents that go into effect only if you are incapacitated and unable to speak for yourself.(8) You can use them to organize and communicate your decisions about things like end-of-life care and organ donation.
Another way to make your decisions known is to carry a wallet card that explains that you have an advance directive and where it is kept.
Give copies of advance care planning documents to your healthcare proxy, your healthcare providers, your hospital, and anyone you think should have the information.
Create digital duplicates of hardcopy documents. Save them in a password-protected format to a flash or external hard drive or a secure cloud service.
Like most important paperwork, advance directive documents, wallet cards, and even online profiles for decisions like organ donation require occasional maintenance. Periodic proofreading for errors and outdated information will save yourself and others time, frustration, and added worry in an emergency.
References
- https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/advance-care-planning-health-care-directives
- https://www.cdc.gov/aging/advancecareplanning/index.htm
- https://www.cdc.gov/aging/advancecareplanning/
- https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/advance-care-planning-health-care-directives
- https://medlineplus.gov/organdonation.html
- https://www.organdonor.gov/learn/organ-donation-statistics
- https://www.organdonor.gov/sign-up
- https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/advance-care-planning-health-care-directives#:~:text=These%20preferences%20are%20often%20put,of%20medical%20care%20you%20want
Resources
- Public Health Matters: Get Involved: Donate Blood. Save Lives.
- Give Peace of Mind: Advance Care Planning
- Advance Care Planning: Health Care Directives
- CDC Transplant Safety
- HRSA Organ Donor
Thanks in advance for your questions and comments on this Public Health Matters post. Please note that CDC does not give personal medical advice. If you are concerned you have a disease or condition, talk to your doctor.
Have a question for CDC? CDC-INFO (http://www.cdc.gov/cdc-info/index.html) offers live agents by phone and email to help you find the latest, reliable, and science-based health information on more than 750 health topics.

 Traumatic events and most emergencies are beyond your control. You can, however, prepare your mental health for the stress of an emergency. Practice self-care, develop coping skills, and make social connections before an emergency happens. Taking care of yourself can also better equip you to take care of others.
Traumatic events and most emergencies are beyond your control. You can, however, prepare your mental health for the stress of an emergency. Practice self-care, develop coping skills, and make social connections before an emergency happens. Taking care of yourself can also better equip you to take care of others. Many children don’t have adult supervision 100% of the time. Parents and caregivers have jobs, errands, and other responsibilities that require them to leave their kids home alone sometimes.
Many children don’t have adult supervision 100% of the time. Parents and caregivers have jobs, errands, and other responsibilities that require them to leave their kids home alone sometimes.
 A “day at the beach” can turn into anything but if you aren’t prepared. Rip currents,
A “day at the beach” can turn into anything but if you aren’t prepared. Rip currents,  First-aid kits make it possible for ordinary people to help until professional help arrives. That’s important because family, friends, coworkers, etc.—not first responders—are often first on the scene in a medical emergency.
First-aid kits make it possible for ordinary people to help until professional help arrives. That’s important because family, friends, coworkers, etc.—not first responders—are often first on the scene in a medical emergency. This
This  Emergency preparedness can be stressful for all families, especially those with
Emergency preparedness can be stressful for all families, especially those with 



