In this paper, published in October in PLOS Pathogens, we discovered a novel genetic association between life-threatening invasive meningococcal disease (IMD) and bacterial genetic variation in factor H binding protein (fHbp) through two bacterial genome-wide association studies (GWAS), which we validated experimentally. This was a collaboration with the groups of Chris Tang and Martin Maiden, with the work in my group led by Sarah Earle.
fHbp is an important component of meningococcal vaccines that directly interacts with human complement factor H (CFH). Intriguingly, our discovery that bacterial genetic variation in fHbp associates with increased virulence mirrors an earlier discovery that human genetic variation in CFH associates with increased susceptibility to IMD (Nature Genetics 42: 772).
Our experiments showed that the fHbp risk allele increased expression. Interestingly, increased susceptibility to IMD has been previously associated with elevated CFH expression. Therefore over-expression of either fHbp by the bacterium or CFH by the host appears to increase the risk of IMD. Since complement evasion is necessary for pathogenesis, these insights offer new leads for improving treatment.
Key results from the paper:
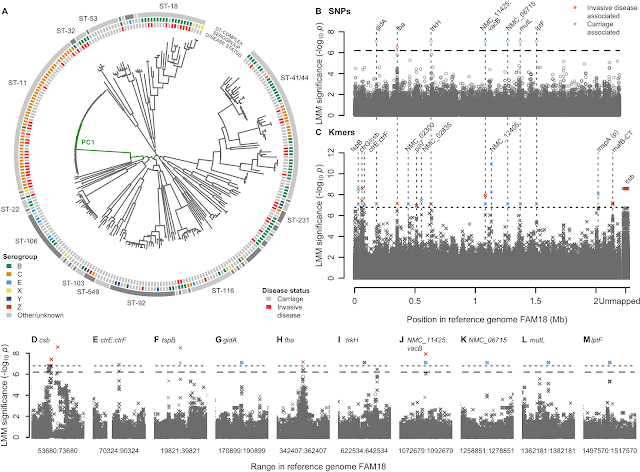
- A GWAS for IMD in 261 meningococci from the Czech Republic highlighted a highly polygenic architecture of meningococcal virulence (see Figure), including capsule biosynthesis genes, the meningococcal disease association island and the new signal near the fba and fHbp genes.
- A replication GWAS for IMD in 1295 meningococcal genomes belonging to strain ST41/44 downloaded from pubMLST.org validated the novel signal of association near fba and fHbp.
- SHAPE reactivity analyses revealed that IMD-associated variation in the regulatory region of fHbp disrupted the ability of the cell machinery to commence gene expression.
- Flow cytometry assays of newly constructed genetically engineered strains, in different temperatures and in the presence and absence of human serum, attributed changes in gene expression to a non-synonymous candidate mutation in the fHbp gene.
In this study, our GWAS relied exclusively on publicly available genome sequences and metadata, highlighting the untapped potential of large-scale open source databases like pubMLST.org, and the value of big data for improving our understanding of disease.