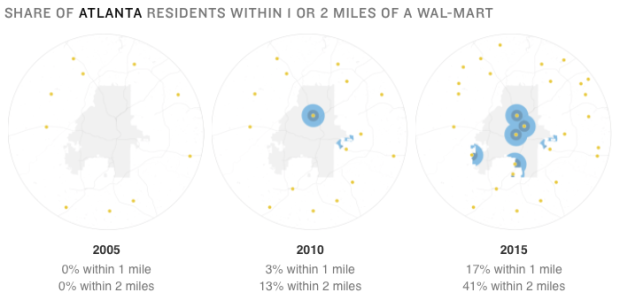
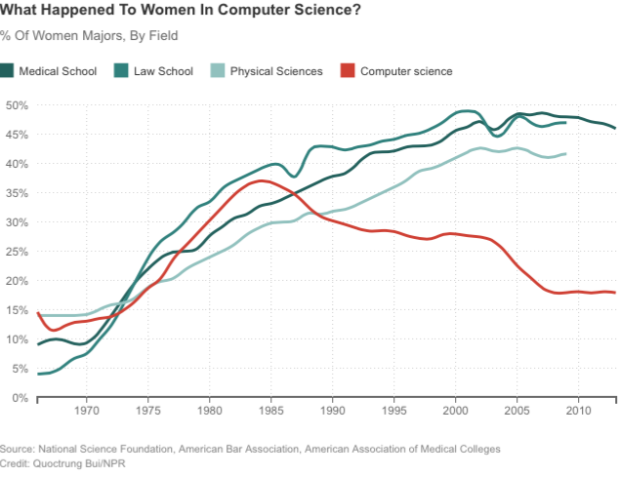
Truth & Quantity by Gregor Hochmuth is what happens when you strip out all context from an NPR newscast and only look at the numbers.
Every day at 8am and 8pm, Truth & Quantity transcribes NPR’s hourly news update using speech recognition & natural language analysis. It then selects all plural nouns from the news script and generates two compilations: one for each month (going back to 2009) and another for various quantities, such as all instances of “7” or “100 million.”
Click on any number to get more of a sentence.
Good stuff. Find out more here.
Tags: natural language, NPR